Distribution Warehouse: A Full-Circle Review of Logistics Hubs
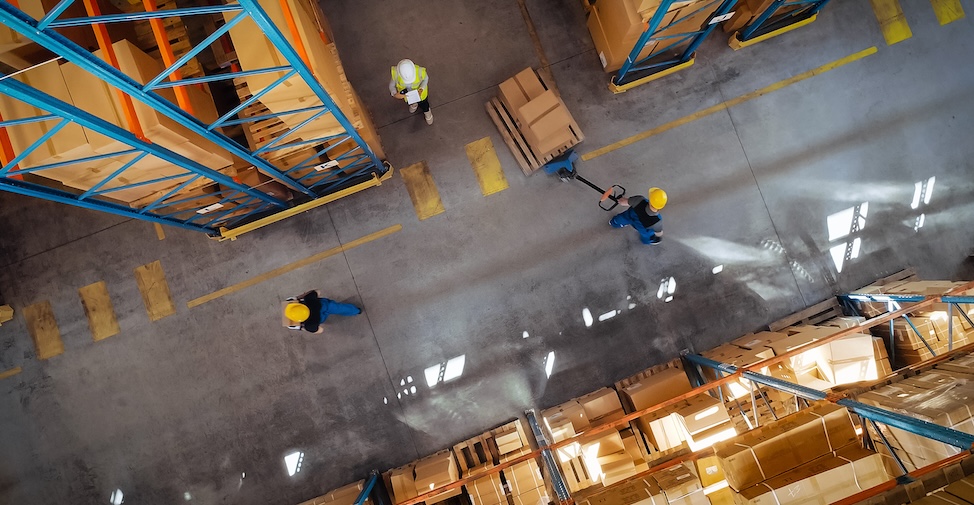

Distribution warehouses are the unsung heroes of the supply chain, playing a crucial role in keeping the wheels of commerce turning. These specialized facilities ensure products reach their destinations efficiently and on time, acting as the backbone of modern logistics.
From receiving and sorting goods to managing inventory and fulfilling orders, distribution warehouses streamline the flow of goods from manufacturers to consumers. Understanding these facilities is essential for businesses of all sizes, as they contribute significantly to operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Distribution warehouses encompass diverse elements, including essential functions, key components, and variations suited to specific industry needs. By examining these aspects, we can gain important insights into the inner operations of these key logistics centers and their influence on worldwide commerce.
As we explore further, we’ll examine the development of distribution warehouses, their strategic placements, and the innovative technologies that power their operations. We’ll also examine the importance of sustainability, safety measures, and workforce management in these ever-changing environments.
Essential Elements of Distribution Warehouses
Distribution warehouses are complex facilities designed to efficiently manage the flow of goods through the supply chain. To grasp their role better, it’s important to explore the key components that make these logistics hubs function effectively.
Location and Accessibility
The strategic placement of distribution warehouses is crucial for their effectiveness. These facilities are typically situated near major transportation hubs such as ports, airports, highway intersections, and railway terminals.
This proximity allows for quick and cost-effective movement of goods. It significantly reduces transit times and transportation costs, enhancing overall efficiency.
Layout and Design
A well-designed distribution warehouse optimizes space utilization and workflow efficiency. Key layout considerations include:
- Receiving areas for incoming shipments
- Storage zones for different types of products
- Packing and shipping stations
- Cross-docking areas for quick transfers
- Office spaces for administrative tasks
The layout should enable smooth product flow, minimize handling, and maximize storage capacity. Thoughtful design can significantly improve operational efficiency and reduce costs.
Types Of Distribution Warehouses
Distribution warehouses come in various forms to cater to different industry needs. Some common types include:
- Public warehouses: Open to multiple businesses
- Private warehouses: Operated by a single company
- Automated warehouses: Utilizing robotics and AI
- Climate-controlled warehouses: For temperature-sensitive goods
Companies like Amertrans Logistics offer customized warehouse and distribution solutions to meet specific business requirements. These customized solutions help businesses optimize their supply chain operations.
Technology and Equipment
Modern distribution warehouses rely heavily on technology to streamline operations. Key technological components include:
- Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
- Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID) tags
- Barcode scanners
- Automated sorting systems
- Conveyors and material handling equipment
These technologies enhance inventory accuracy, speed up order processing, and improve overall efficiency. They play a crucial role in maintaining competitiveness in today’s fast-paced logistics environment.
Workforce and Expertise
A skilled workforce is essential for smooth warehouse operations. Key roles include:
- Warehouse managers
- Inventory specialists
- Forklift operators
- Pickers and packers
- Quality control inspectors
Ongoing training ensures that staff can adapt to new technologies and maintain high standards of efficiency and safety. A well-trained workforce is the backbone of any successful distribution warehouse.
Safety and Compliance
Distribution warehouses must adhere to strict safety regulations and industry standards. These include:
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) guidelines
- Fire safety protocols
- Proper handling of hazardous materials
- Regular safety training for employees
Compliance with these standards protects workers, preserves inventory, and maintains the warehouse’s operational integrity. It’s not just about following rules; it’s about creating a safe and efficient working environment.
By incorporating these critical components, distribution warehouses serve as important connections in the supply chain. They enable businesses to meet customer demands efficiently and cost-effectively, playing a crucial role in modern commerce.
The Evolution Of Distribution Warehouses
Distribution warehouses have undergone significant transformation over the years, adapting to changing market demands and technological advancements. This evolution has profoundly impacted modern logistics, reshaping the way businesses handle storage and distribution.
Traditional Warehouses
Traditional warehouses were simple storage facilities with basic structures for holding inventory. They relied on manual processes for receiving, storing, and shipping goods, with limited technology and a heavy dependence on paper-based systems.
These warehouses focused primarily on long-term storage. Unfortunately, they were often inefficient, resulting in slow order processing and frequent inventory discrepancies.
Emergence of Distribution Centers
As businesses grew and supply chains became more complex, distribution centers emerged, marking a shift from pure storage to active distribution. These centers introduced basic inventory management systems and improved layouts for faster order fulfillment.
Connecting to transportation networks was a crucial aspect of this development. This development marked the beginning of more strategic approaches to warehousing and distribution.
Modern Distribution Warehouses
Today’s distribution warehouses are highly sophisticated operations featuring advanced automation and robotics. They employ real-time inventory tracking and management systems, seamlessly integrating with e-commerce platforms.
These modern facilities focus on speed and accuracy in order fulfillment. They incorporate sustainable practices and energy-efficient designs to meet the demands of omnichannel retail and just-in-time inventory management.
Technological Advancements
Technology has been a key driver in the evolution of distribution warehouses, with Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) streamlining operations. The Internet of Things (IoT) has enhanced tracking and monitoring capabilities, while Artificial Intelligence (AI) enables predictive analytics and demand forecasting.
Autonomous vehicles and drones are now used for internal transportation. These technological advancements have dramatically improved efficiency, accuracy, and speed in warehouse operations.
Changing Customer Expectations
The evolution of distribution warehouses has been largely driven by changing customer demands, including faster delivery times and greater product variety. Customers now expect seamless returns processes and transparency in order tracking.
Modern distribution warehouses are designed to meet these expectations, often serving as the backbone of e-commerce operations. They play a crucial role in satisfying the ever-increasing demands of today’s consumers.
Future Trends
The evolution of distribution warehouses continues, with several emerging trends shaping their future. These include increased use of augmented reality for picking and training, and a greater emphasis on sustainability and eco-friendly practices.
Collaboration with urban micro-fulfillment centers and the implementation of blockchain technology for improved traceability are also on the horizon. These trends suggest that distribution warehouses will continue to play a crucial role in shaping the future of logistics and supply chain management.
Distribution warehouses remain at the forefront of innovation in the logistics industry, constantly adapting to meet the changing needs of businesses and consumers alike. The continuous evolution of supply chain management promises to bring even greater efficiency and sophistication to this domain.
Strategic Location And Design
The success of a distribution warehouse heavily relies on its strategic location and thoughtful design. These factors significantly impact operational efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and the ability to meet customer demands.
Choosing the Right Location
Selecting an optimal location for a distribution warehouse involves considering several key factors. These include:
-
- Proximity to major transportation hubs (airports, seaports, highways)
- Accessibility to target markets
- Labor availability and costs
- Local regulations and zoning laws
- Potential for future expansion
A well-chosen location can reduce transportation costs, improve delivery times, and enhance overall supply chain efficiency.
Layout and Space Utilization
Effective warehouse design maximizes space utilization and streamlines operations. Key considerations include:
- Optimized floor plans for efficient product flow
- Strategic placement of loading docks and staging areas
- Adequate aisle width for equipment maneuverability
- Vertical space utilization with high-bay racking systems
- Designated areas for value-added services (e.g., packaging, labeling)
A well-designed layout minimizes travel time within the warehouse, reduces handling costs, and improves order accuracy.
Technology Integration
Modern distribution warehouses incorporate advanced technologies to enhance operations. These technologies include:
- Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS)
- Conveyor systems and sortation equipment
- Radio-frequency identification (RFID) for inventory tracking
- Pick-to-light and voice-picking systems
- Connecting warehouse management systems (WMS) with enterprise resource planning (ERP) software
These technological advancements improve accuracy, speed, and overall warehouse productivity.
Sustainability Considerations
Environmentally friendly design is becoming increasingly important in distribution warehouses. Key sustainability measures include:
- Energy-efficient lighting and HVAC systems
-
- Use of renewable energy sources (e.g., solar panels)
- Water conservation measures
- Recycling and waste reduction programs
- Green building materials and practices
Sustainable design not only reduces environmental impact but can also lead to long-term cost savings.
Flexibility and Scalability
Distribution warehouses must be designed with future growth in mind. Important aspects of flexibility and scalability include:
-
- Modular designs that allow for easy reconfiguration
- Scalable technology systems
- Multi-purpose spaces that can adapt to changing needs
- Provisions for potential automation upgrades
- Expandable storage solutions
Flexibility in design ensures that the warehouse can adapt to changing business needs and market demands.
Safety and Security Measures
Prioritizing safety and security is crucial in warehouse design. Essential measures include:
- Clear traffic lanes and pedestrian walkways
-
- Adequate lighting throughout the facility
- Fire suppression systems and emergency exits
- Secure storage areas for high-value items
- Access control systems and surveillance cameras
These measures protect both employees and inventory, reducing risks and potential losses.
Employee Comfort and Productivity
Considering the human element in warehouse design is essential for optimal performance. Key factors include:
-
- Ergonomic workstations and equipment
- Comfortable break areas and restrooms
- Proper ventilation and temperature control
-
- Natural lighting where possible
- Clear signage and wayfinding
A comfortable work environment leads to increased employee satisfaction and productivity.
By carefully considering these aspects of strategic location and design, distribution warehouses can optimize their operations, reduce costs, and better serve their customers’ needs. The right combination of location, layout, and technology creates a foundation for efficient and effective warehouse management.
Operations And Processes
The heart of a distribution warehouse lies in its operations and processes. These well-orchestrated activities ensure the smooth flow of goods from receipt to dispatch.
Receiving and Sorting
When goods arrive at a distribution warehouse, the receiving process begins. This crucial step involves several key activities:
- Verification of incoming shipments against purchase orders
- Quality inspection of received goods
- Sorting items based on product type, destination, or storage requirements
- Updating inventory records in real-time
- Assigning storage locations for efficient retrieval
Efficient receiving and sorting lay the foundation for all subsequent warehouse operations.
Inventory Management
Effective inventory management is critical for warehouse success. Key strategies include:
- Implementing cycle counting for accurate stock levels
- Using ABC analysis to prioritize high-value or fast-moving items
- Applying FIFO (First-In-First-Out) or LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) methods as appropriate
- Utilizing barcode or RFID technology for real-time tracking
- Maintaining optimal stock levels to balance demand and storage costs
Proper inventory management ensures product availability while minimizing carrying costs.
Order Fulfillment
The order fulfillment process is where customer satisfaction begins. It encompasses several crucial steps:
- Receiving and processing customer orders
- Picking items from storage locations
- Consolidating multi-item orders
- Packing orders securely and efficiently
- Generating shipping labels and documentation
- Quality checking to ensure order accuracy
Streamlined order fulfillment processes reduce errors and improve delivery times.
Shipping And Transportation Coordination
Coordinating shipping and transportation is crucial for timely deliveries. Essential activities include:
- Selecting appropriate shipping methods based on order requirements
- Scheduling pickups with carriers
- Optimizing load planning for efficient use of transportation
- Tracking shipments and providing updates to customers
- Offering options for expedited shipping when needed
Effective coordination ensures that products reach their destinations on time and in good condition.
Returns Processing
Managing returns is a crucial component of warehouse operations. Key steps in this process include:
-
- Receiving and inspecting returned items
- Determining the condition and resale potential of returns
- Restocking sellable items
- Processing refunds or exchanges
- Disposing of or recycling unsellable items
Efficient returns processing can recover value and improve customer satisfaction.
Value-Added Services
Many distribution warehouses offer additional services to enhance product value. These may include:
-
- Kitting and assembly of product bundles
- Custom packaging and labeling
- Light manufacturing or final assembly
- Quality control inspections
- Product customization or personalization
These services can differentiate a warehouse and provide additional revenue streams.
Continuous Improvement
Successful warehouses constantly seek ways to enhance their operations. This involves:
- Analyzing key performance indicators (KPIs)
- Implementing lean management principles
- Conducting regular staff training and development
- Staying updated on industry trends and technologies
- Soliciting and acting on customer feedback
Continuous improvement ensures that the warehouse remains competitive and efficient.
Compliance and Quality Assurance
Maintaining compliance and quality standards is essential. Key aspects include:
- Adhering to industry-specific regulations (e.g., FDA, OSHA)
- Implementing quality management systems (e.g., ISO 9001)
- Conducting regular audits and inspections
- Maintaining proper documentation and record-keeping
- Ensuring product traceability throughout the supply chain
Compliance and quality assurance protect the warehouse, its clients, and end consumers.
By mastering these operations and processes, distribution warehouses can ensure efficient, accurate, and timely handling of goods. This operational excellence translates into satisfied customers, reduced costs, and a competitive advantage in the dynamic field of logistics and supply chain management.
Technology In Modern Distribution Warehouses
Technology plays a pivotal role in enhancing the efficiency and accuracy of distribution warehouses in today’s rapidly evolving logistics environment.
From automated systems to data-driven decision-making tools, modern warehouses utilize cutting-edge technologies to streamline operations and meet growing customer demands.
Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Warehouse Management Systems are the backbone of modern distribution centers. These systems offer a range of essential features:
- Real-time inventory tracking and management
- Order processing and fulfillment optimization
- Labor management and task allocation
- Performance analytics and reporting Connecting with other business systems (ERP, TMS)
A robust WMS improves accuracy, reduces errors, and enhances overall warehouse productivity.
Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS)
AS/RS technology revolutionizes how goods are stored and retrieved. These systems offer numerous benefits:
- High-density storage utilization
- Reduced labor costs and improved safety
- Increased accuracy in inventory management
- Faster order fulfillment times
- Scalability to accommodate business growth
AS/RS is particularly beneficial for warehouses dealing with high volumes of small to medium-sized items.
Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation are transforming warehouse operations. Key technologies include:
- Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) for material transport
- Robotic arms for picking and packing
- Collaborative robots (cobots) working alongside human workers
- Conveyor systems for efficient product movement
- Automated sorters for rapid order processing
These technologies enhance speed, accuracy, and consistency in warehouse tasks.
Internet of Things (IoT) and Sensors
IoT devices and sensors provide real-time data and insights for various applications:
- Environmental monitoring (temperature, humidity)
- Asset tracking and management
- Predictive maintenance for equipment
- Energy consumption optimization
- Safety and security enhancements
IoT technology enables proactive decision-making and improved operational efficiency.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning drive smarter warehouse operations through:
- Demand forecasting and inventory optimization
- Intelligent route planning for order picking
- Anomaly detection in processes and quality control
- Automated decision-making for task prioritization
- Continuous process improvement through data analysis
These technologies help warehouses adapt to changing conditions and improve over time.
Cloud Computing and Big Data Analytics
Cloud-based solutions and big data analytics offer powerful insights for warehouse management:
- Scalable storage and processing capabilities
- Real-time data access and sharing across locations
- Advanced analytics for performance optimization
- Improved visibility across the supply chain
- Enhanced collaboration with partners and customers
Leveraging cloud and data technologies enables warehouses to make data-driven decisions and improve overall performance.
Mobile and Wearable Technology
Mobile devices and wearables enhance worker productivity through various tools:
- Handheld scanners for inventory management
- Voice-directed picking systems
- Smart glasses for augmented reality picking
- Wearable devices for worker safety monitoring
- Mobile apps for real-time communication and task management
These technologies improve accuracy, speed, and worker satisfaction in warehouse operations.
Blockchain for Supply Chain Transparency
Blockchain technology is emerging as a tool for enhancing supply chain transparency. Its potential benefits include:
- Improved traceability of products
- Enhanced security and fraud prevention
- Streamlined documentation and paperwork
- Increased trust among supply chain partners
- Simplified auditing and compliance processes
While still in early stages of adoption, blockchain has the potential to revolutionize supply chain management in distribution warehouses.
By embracing these technological advancements, modern distribution warehouses can significantly improve their operational efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability. As technology continues to advance, warehouses that stay at the forefront of innovation will be best positioned to meet the challenges of tomorrow’s supply chain demands.
Sustainability In Distribution Warehouses
Environmental concerns are driving distribution warehouses to focus on sustainability. By implementing eco-friendly practices, these facilities reduce their environmental impact while often realizing cost savings and improved operational efficiency.
Energy Efficiency Measures
Distribution warehouses are adopting various energy-efficient solutions:
- LED lighting systems with motion sensors
- High-efficiency HVAC systems
- Improved insulation for temperature control
- Energy management systems for optimized consumption
- Solar panels for renewable energy generation
These measures significantly reduce energy consumption and associated costs.
Sustainable Building Design
Modern warehouse design incorporates sustainability from the ground up:
- Green building materials and construction methods
- Skylights and windows for natural lighting
- Rainwater harvesting systems
- Green roofs for improved insulation
- Permeable paving to reduce stormwater runoff
Sustainable design not only reduces environmental impact but can also improve worker comfort and productivity.
Waste Reduction and Recycling Programs
Effective waste management is crucial for sustainable warehouse operations:
- Extensive recycling programs for packaging materials
- Reusable packaging solutions
- Composting of organic waste
- Partnerships with recycling facilities
- Employee education on waste reduction
These initiatives minimize landfill waste and can often generate additional revenue streams.
Sustainable Transportation and Logistics
Warehouses are optimizing transportation to reduce emissions:
- Electric or hybrid vehicles for short-distance transport
- Route optimization software to reduce fuel consumption
- Encouraging consolidation of shipments
- Partnerships with eco-friendly logistics providers
- Implementation of reverse logistics for efficient returns management
Sustainable transportation practices lead to reduced carbon footprint and often lower operational costs.
Water Conservation Strategies
Water-saving measures are becoming increasingly important:
- Low-flow fixtures in bathrooms and kitchens
- Drought-resistant landscaping
- Water recycling systems for non-potable uses
- Regular maintenance to prevent leaks
- Rainwater collection for irrigation
These strategies reduce water consumption and associated utility costs.
Green Packaging Solutions
Sustainable packaging is a key focus area:
- Biodegradable or recyclable packaging materials
- Minimalist packaging design to reduce material use
- Reusable containers for internal operations
- Packaging made from recycled content
- Elimination of single-use plastics
Green packaging reduces waste and can enhance brand image with environmentally conscious consumers.
Employee Engagement in Sustainability
Engaging employees is crucial for successful sustainability initiatives:
- Sustainability training programs
- Green teams to champion eco-friendly practices
- Incentives for sustainable behavior
- Regular communication of sustainability goals and achievements
- Encouraging employee suggestions for sustainability improvements
Employee involvement ensures that sustainability becomes ingrained in the warehouse culture.
Sustainable Inventory Management
Efficient inventory management contributes to sustainability:
- Just-in-time inventory practices to reduce waste
- FIFO (First-In-First-Out) systems to minimize product expiration
- Use of sustainable products in warehouse operations
- Donation programs for excess inventory
- Implementing circular economy principles
These practices reduce waste and improve resource utilization.
Certifications and Compliance
Many warehouses are pursuing sustainability certifications:
- LEED (Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design) certification
- ISO 14001 Environmental Management System
- BREEAM (Building Research Establishment Environmental Assessment Method)
- Energy Star certification
- Local and regional sustainability compliance programs
These certifications demonstrate commitment to sustainability and can provide a competitive advantage.
Distribution warehouses can significantly reduce their environmental impact while improving operational efficiency and reducing costs through sustainable practices.
As sustainability gains importance for consumers and businesses, warehouses prioritizing eco-friendly practices will be well-positioned for future success in the logistics industry.
Safety And Security Measures
Distribution warehouses prioritize maintaining a safe and secure environment to protect employees, safeguard inventory, and ensure smooth operations. Let’s explore the key safety and security measures implemented in modern distribution warehouses.
Employee Safety Protocols
Prioritizing employee safety is crucial in warehouse operations. Key measures include extensive safety training programs, Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) requirements, regular safety drills, emergency preparedness exercises, clear signage, floor markings for traffic management, and ergonomic workstations to prevent repetitive strain injuries.
Fire Prevention and Response
Fire safety is a critical concern in warehouses. Essential measures include state-of-the-art fire detection and suppression systems, regular fire safety inspections and maintenance, clearly marked fire exits and evacuation routes, fire-resistant storage solutions for hazardous materials, and employee training on fire prevention and response.
Access Control Systems
Controlling access is essential for warehouse security. Effective systems include biometric entry systems, key card access for different security levels, visitor management protocols, secure loading docks with controlled access, and restricted areas for high-value or sensitive items.
Surveillance and Monitoring
Extensive surveillance maintains constant vigilance in distribution warehouses. Key components include comprehensive CCTV coverage of all warehouse areas available around the clock, advanced video analytics to detect unusual activities, coordination with access control systems, regular security patrols, and remote monitoring capabilities.
Inventory Security Measures
Protecting inventory is a top priority in distribution warehouses. Important measures include RFID tracking for high-value items, secure storage areas with limited access, regular inventory audits and cycle counts, tamper-evident packaging for sensitive products, and serialization and barcoding for improved traceability.
Cybersecurity Protocols
In the modern era, safeguarding information is as vital as physical security. Robust cybersecurity measures include firewalls and intrusion detection systems, regular software updates and patch management, employee training on cybersecurity best practices, secure encrypted communication channels, and regular security audits and penetration testing.
Emergency Response Planning
Being prepared for emergencies is critical in distribution warehouses. Essential elements include detailed emergency response plans for various scenarios, designated emergency response teams, first aid stations and AED placement, coordination with local emergency services, and regular drills and plan updates.
Environmental Health and Safety Compliance
Adhering to regulations ensures a safe working environment in distribution warehouses.
Key aspects include regular safety inspections and audits, proper handling and storage of hazardous materials, compliance with OSHA standards and local regulations, environmental impact assessments, and proper waste management and disposal procedures.
Equipment Safety Measures
Ensuring the safe operation of warehouse equipment is crucial. Important measures include regular maintenance and safety checks on forklifts and other machinery, operator certification and training programs, safety interlocks and emergency stop mechanisms on equipment, clear operational guidelines and safety procedures, and proper storage and charging areas for powered equipment.
Health and Wellness Programs
Promoting employee health contributes to overall safety in distribution warehouses. Effective programs include ergonomic assessments and workstation adjustments, stress management and mental health support, fitness programs and wellness challenges, health screenings and vaccinations, and proper ventilation and air quality management.
By implementing these robust safety and security measures, distribution warehouses establish a secure environment that safeguards employees, inventory, and operations. This approach not only ensures compliance with regulations but also builds trust with clients and enhances overall operational efficiency.
As technology evolves, warehouses continue to adopt new and innovative security solutions to stay ahead of potential threats and maintain a safe working environment. The ongoing commitment to safety and security in distribution warehouses reflects the industry’s dedication to creating a secure and efficient supply chain ecosystem.
Cost Considerations and ROI
Understanding the financial aspects of operating a distribution warehouse is crucial for businesses looking to optimize their supply chain. Let’s explore the key cost considerations and potential return on investment (ROI) associated with distribution warehouses.
Initial Setup Costs
Setting up a distribution warehouse requires significant upfront investment. This includes land acquisition or leasing, building construction or renovation, warehouse management systems (WMS) implementation, equipment purchases (forklifts, conveyor belts, racking systems), and security system installation.
Operational Expenses
Ongoing operational costs include labor (wages, benefits, training), utilities (electricity, water, heating/cooling), maintenance and repairs, insurance premiums, property taxes, and inventory carrying costs. Effective management of these expenses is key to maintaining profitability.
Technology Investments
Investing in technology can improve efficiency and reduce long-term costs. This includes automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS), robotics and AI-powered solutions, IoT devices for real-time tracking, cloud-based inventory management software, and data analytics tools.
Scalability and Flexibility
Consider costs associated with future growth, such as modular racking systems for easy reconfiguration, expandable warehouse management systems, flexible workforce management, and adaptable transportation networks. Planning for scalability can reduce future expansion costs and improve ROI.
Energy Efficiency Measures
Implementing energy-efficient solutions can lead to long-term savings. These include LED lighting systems, solar panel installations, high-efficiency HVAC systems, energy management systems, and insulation improvements.
Outsourcing vs. In-house Operations
Weigh the costs of outsourcing against managing in-house operations. Consider third-party logistics (3PL) provider fees, control over operations and quality, flexibility in scaling operations, capital investment requirements, and risk management considerations.
Location Considerations
The warehouse location significantly impacts costs and efficiency. Factors to consider include proximity to suppliers and customers, transportation infrastructure access, labor market availability and costs, local tax incentives and regulations, and real estate prices and availability.
Inventory Optimization
Efficient inventory management improves ROI through just-in-time (JIT) inventory systems, demand forecasting tools, cross-docking capabilities, vendor-managed inventory (VMI) programs, and ABC analysis for stock prioritization. Optimizing inventory levels reduces carrying costs and improves cash flow.
Performance Metrics and KPIs
Tracking key performance indicators (KPIs) helps measure ROI. Important metrics include order fulfillment rates, inventory turnover ratio, picking accuracy, labor productivity, and on-time shipping percentage.
Risk Management and Insurance
Mitigating risks can prevent costly disruptions. This involves extensive insurance coverage, business continuity planning, cybersecurity measures, safety and compliance programs, and diversification of suppliers and customers.
Return on Investment Calculation
To determine the ROI of your distribution warehouse, calculate total costs (initial setup + operational expenses), estimate revenue generated or cost savings achieved, and use the formula: ROI = (Net Profit / Total Investment) x 100. Consider both short-term and long-term ROI when making investment decisions.
Cost Reduction Strategies
Implement strategies to improve ROI, such as lean management principles, continuous improvement programs, strategic partnerships with suppliers, employee training and development, and regular cost audits and benchmarking.
Continuously seeking ways to reduce costs while maintaining quality is crucial for long-term success.
By carefully considering these cost factors and focusing on maximizing ROI, businesses can create efficient and profitable distribution warehouse operations.
The key is to balance initial investments with long-term operational efficiency, always keeping an eye on emerging technologies and industry best practices.
Workforce Management in Distribution Centers
Effective workforce management is crucial for the smooth operation of distribution centers. Let’s examine the key aspects of managing personnel in these evolving work environments.
Hiring and Recruitment
Attracting and retaining skilled workers is essential for distribution center success. To achieve this, develop clear job descriptions and requirements, and utilize multiple recruitment channels such as job boards, social media, and referrals.
- Implement pre-employment assessments to ensure candidate fit
- Offer competitive wages and benefits packages
- Create a positive employer brand to attract top talent
Training and Development
Continuous learning is essential in the ever-evolving logistics industry. Offer thorough onboarding programs for new employees and provide regular safety training to help prevent workplace incidents.
- Implement cross-training initiatives to increase workforce flexibility
- Develop leadership programs to nurture future managers
- Utilize e-learning platforms for ongoing skill development
Shift Planning and Scheduling
Efficient scheduling is key to meeting demand while managing labor costs. Use workforce management software for data-driven scheduling and implement flexible shift patterns to accommodate peak periods.
- Consider part-time and temporary staff to manage fluctuations
- Ensure compliance with labor laws and regulations
- Encourage open communication for shift swaps and time-off requests
Performance Management
Monitoring and improving employee performance drives productivity. Set clear performance expectations and KPIs, and conduct regular performance reviews and feedback sessions.
- Implement incentive programs to reward high performers
- Address underperformance promptly and constructively
- Use data analytics to identify trends and areas for improvement
Health and Safety
Prioritizing worker well-being is crucial in warehouse environments. Conduct regular safety audits and risk assessments, and provide appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
- Implement ergonomic workstations and equipment
- Offer wellness programs to promote overall health
- Maintain clear emergency procedures and conduct drills
Employee Engagement and Retention
Cultivating a positive work environment reduces turnover. Encourage open communication between management and staff, and recognize and celebrate employee achievements.
- Provide opportunities for career advancement
- Conduct regular employee satisfaction surveys
- Implement team-building activities to boost morale
Diversity and Inclusion
Creating an inclusive workplace enhances innovation and productivity. Develop diversity recruitment strategies and provide diversity and inclusion training for all employees.
- Establish employee resource groups
- Ensure equal opportunities for advancement
- Celebrate cultural diversity in the workplace
Technology Integration
Leveraging technology improves workforce efficiency. Implement warehouse management systems (WMS) for task allocation and use wearable devices for real-time communication and tracking.
- Adopt mobile apps for time and attendance management
- Utilize AI-powered tools for workforce forecasting
- Implement robotics and automation to support human workers
Labor Relations
Maintaining positive relationships with unions and workers is essential. Encourage open dialogue with union representatives and ensure adherence to collective bargaining agreements.
- Address grievances promptly and fairly
- Involve employees in decision-making processes
- Stay informed about labor laws and regulations
Workforce Analytics
Data-driven insights can optimize workforce management. Track key metrics such as productivity, attendance, and turnover, and use predictive analytics for demand forecasting and staffing.
- Identify trends and patterns in workforce performance
- Make informed decisions on training and development needs
- Continuously refine workforce strategies based on data insights
Succession Planning
Preparing for the future ensures continuity in leadership. Identify high-potential employees for leadership roles and develop mentorship programs to transfer knowledge.
- Create individual development plans for key positions
- Conduct regular talent reviews and assessments
- Establish clear career paths within the organization
Change Management
Effectively managing organizational changes is crucial. Communicate changes clearly and transparently, and provide training and support for new processes or technologies.
- Address employee concerns and resistance proactively
- Involve employees in the change process when possible
- Monitor and evaluate the impact of changes on workforce performance
By focusing on these aspects of workforce management, distribution centers can create a productive, engaged, and skilled workforce. This not only improves operational efficiency but also contributes to overall business success.
Frequently Asked Questions
- How does a distribution warehouse differ from a traditional warehouse?
Distribution warehouses prioritize efficient goods movement, focusing on rapid receiving, sorting, and shipping to various destinations.
They often employ advanced technology for inventory management and order fulfillment, while traditional warehouses primarily store inventory for longer periods with less emphasis on quick turnaround times.
- What are the main benefits of using a distribution warehouse for businesses?
Distribution warehouses offer improved inventory management, faster order fulfillment, reduced transportation costs, enhanced supply chain efficiency, and scalable operations.
They also provide specialized services like cross-docking, value-added services, and real-time inventory tracking, allowing businesses to optimize logistics, reduce overhead costs, and improve customer satisfaction through faster and more accurate deliveries.
- How do distribution warehouses handle returns and reverse logistics?
Distribution warehouses manage returns and reverse logistics through dedicated processes for receiving, inspecting, and processing returned items in designated areas.
They sort items based on condition and resale potential, restocking sellable items, refurbishing damaged products, or disposing of unsalvageable goods, often using specialized software to track returns, manage inventory, and streamline the entire reverse logistics process.
- Can small businesses benefit from using distribution warehouses?
Small businesses can significantly benefit from distribution warehouses, which offer scalable solutions providing access to professional logistics services without large capital investments.
These facilities help small businesses expand market reach, improve order fulfillment speed, reduce shipping costs, manage seasonal demand fluctuations, and provide expertise in inventory management and shipping, allowing owners to focus on their primary business activities.
- What role do distribution warehouses play in reducing carbon footprints?
Distribution warehouses contribute to reducing carbon footprints by optimizing shipping routes, consolidating shipments, and implementing energy-efficient technologies like LED lighting and solar panels.
They use advanced inventory management systems to minimize waste and optimize stock levels, and are often strategically located near transportation hubs to reduce overall travel distances for goods, helping businesses minimize their environmental impact through centralized operations and improved logistics efficiency.
Conclusion
Distribution warehouses serve as the cornerstone of modern supply chains, playing a crucial role in efficiently moving goods from manufacturers to consumers. These specialized facilities offer a range of services that streamline logistics operations and enhance overall business performance, going far beyond simple storage.
From receiving and sorting goods to managing inventory and fulfilling orders, distribution warehouses are essential in meeting the demands of today’s fast-paced commerce. By leveraging their capabilities, businesses of all sizes can optimize operations, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction.
The advanced technology and strategic processes employed in these facilities enable faster order fulfillment, more accurate inventory management, and efficient handling of returns. Distribution warehouses contribute to sustainability efforts by consolidating shipments and implementing energy-efficient practices.
As the e-commerce industry continues to transform, the significance of distribution centers will only increase. Businesses that effectively utilize these facilities position themselves for success in an increasingly competitive market.
Whether you’re a small business owner seeking to expand your customer base or a consumer curious about the journey of your online purchases, understanding the function and importance of distribution warehouses offers valuable insight into the intricate landscape of modern logistics.
The impact of these facilities extends far beyond the warehouse walls, shaping the way we shop, receive goods, and conduct business in the modern era.
Related Articles
General
Inbound Logistics Explained: Processes, Benefits & Best Practices
Efficiency is the cornerstone of business success in today’s competitive environment. Inbound logistics, a critical component of supply chain management, plays a pivotal role in determining a company’s operational effectiveness and overall performance. Inbound logistics encompasses the processes involved in receiving, storing, and distributing raw materials, components, or finished goods from suppliers to production facilities […]
Read MoreGeneral
Freight Shipping vs. Standard Shipping: Understanding the Difference

Freight shipping stands as a cornerstone of modern logistics, propelling the global economy forward through the efficient movement of goods. This essential component of commerce encompasses the transportation of large quantities of products, distinguishing itself from standard shipping methods in scale, complexity, and significance. Understanding freight shipping is essential for business owners aiming to optimize […]
Read More
